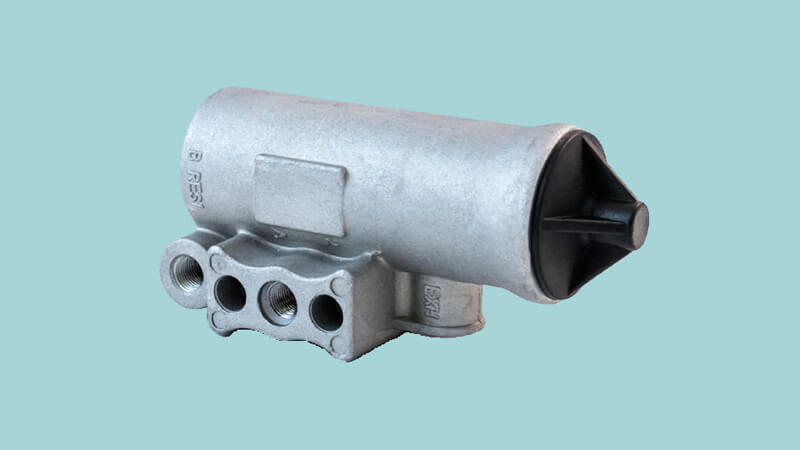
The Governor of an air compressor is a small engine connected to the main engine in a semi-tractor. When the big engine runs, it also starts running and converts mechanical power inputted from a motor into fluid air power. You can store compressed air in a compressed air tank for later use or transfer it via pipes to the location where it is needed.
While the engine operates, the reciprocal air compressor runs continually, but the Governor manages the actual compression.
However, you might get confused about the operations of an air governor as they are available in different types. Also, each type operates differently. So, we have prepared this article discussing about what does the air compressor governor do in detail. Have a look!
The Operations Different Types of An Air Compressor Governor
Compressing elements are called reciprocal compressors. Veins or impellers can also be used to create compressors. Several types of compressors operate differently from each other. Let’s continue with an overview to understand its operation better.
Type of Air Compressor Governor
Usually, the compressors used in automation and the workplace are known as positive displacement compressors. Anytime air is sucked into a chamber while the chamber’s volume is decreased, the pressure is too high. Now we will confine ourselves to two types of air compressors.
- Positive displacement air compressors
- Dynamic air compressors
1. Positive Displacement Air Compressor and Its Operations
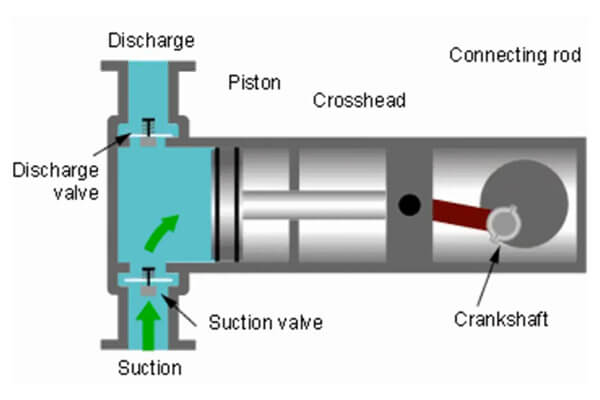
In positive displacement air compressors, the air is brought into a chamber and compressed until a set pressure is reached through mechanical motion. Then, a valve is used to discharge the compressed air at the rated pressure, resulting in airflow. Also, there are three kinds of available positive displacement air compressors. And all of them operate on the same principle. They are:
Rotary Compressor
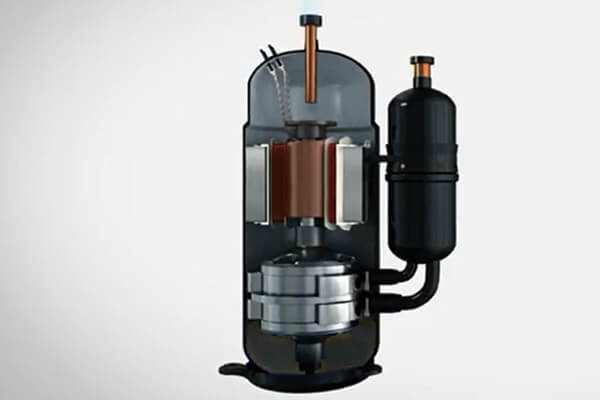

The most popular compressor used nowadays is the rotary positive displacement compressor. Two rotating rotors that continuously pass through the hollow draw air in, seal the entrance, and compress the air. The air is progressively compressed with each turn until it reaches the expected pressure.
Rotating compressors typically have an inlet, an outlet, and a cylindrical housing with adjustable rotary vanes. In addition, on an off-center drive shaft, there are vanes.
The vanes slid in and out as the shaft rotated to keep in touch with the cylindrical compressor wall. They do this by forming chambers inside various-sized cylinders.
Related: Get the Size of Air Compressor with CFM/PSI to Paint Your Car Right Now!
Air enters the most significant chamber. The vanes retract as they revolve, shrinking the chamber and condensing the air. In the tiniest chamber, the air axis. The vibration and pulsation that occur with reciprocating compression are generally free of rotary compressors.
Reciprocating Pistol Compressors
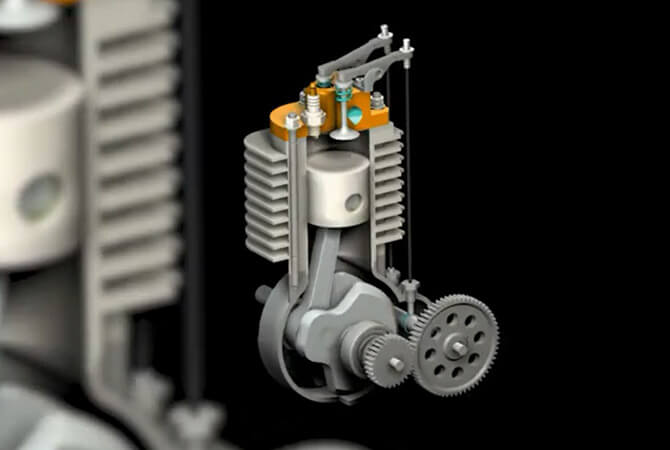
The piston of this type of compressor pulls in air and then compresses it in a constant motion. As the crankshaft rotates, the cylindrical housing reciprocates. The inlet valve allows atmospheric air to enter the cylinder. This is done during the suction stroke of a cylinder. The outlet or discharge valve opens under high pressure during the compression strike. When air is compressed, it becomes warmer.
That is a problem for each compressor. To achieve higher pressures, you would use a two-stage compressor. The large piston builds in the first stage. Therefore, the air leaving the first stage can be cooled before it enters the second stage.
With a two-stage compressor, you can achieve a pressure of over 20 bars or 290 psi. Based on its operation principle, the reciprocating compressor delivers only pulsed compressed air. Therefore, this kind of compressor is used in conjunction with a tank.
Diaphragm Compressor
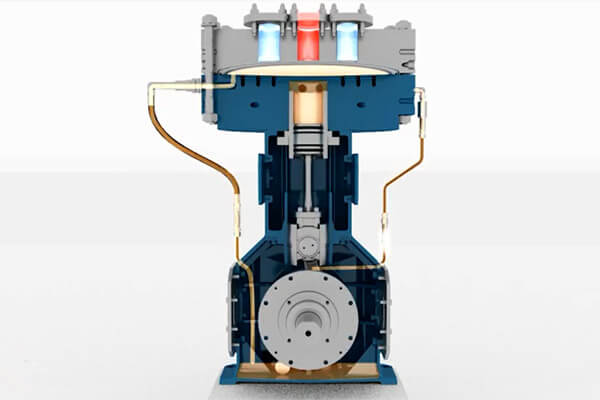
Diaphragm compressors belong to the class of piston compressors. The diaphragm seals off suction chamber from piston diaphragm. As an advantage, the compressed air in the compression chamber does not come into contact with the lubricant piston and thus can be kept free of oil. For example, the food industry or filling diver ‘bottles can use the diaphragm compressor.
2. Dynamic Compressor and Its Operations
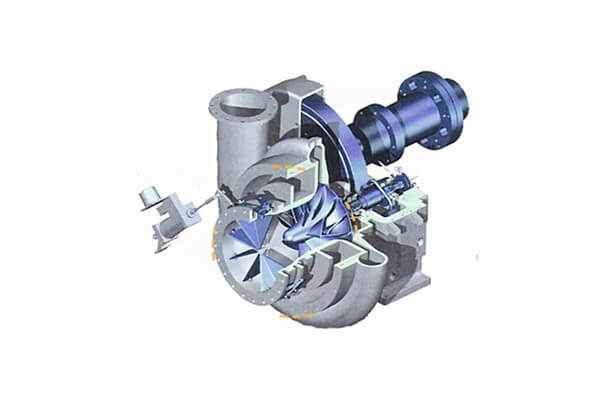

Dynamic compressors are rotational continuous-flow devices. Where the air is accelerated as it passes through the quickly revolving element, transforming the velocity head into pressure, partially in the moving element and partially in stationary diffusers or blades. Dynamic compressors vary significantly in capacity based on their working pressure.
Air Compressor Governor Unloader
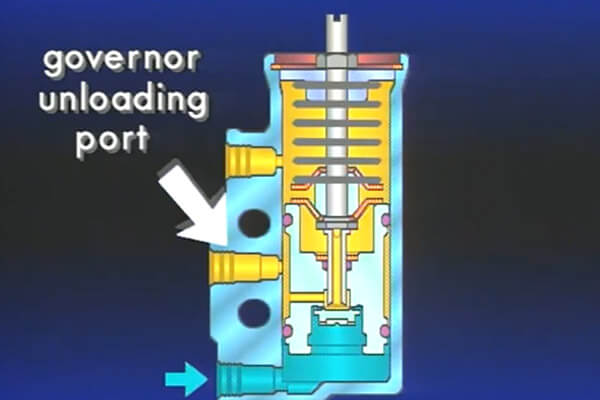
The UNLOADER assembly, located in the compressor head, is controlled by the Governor. Poppet-style or spring-loaded control valves are also acceptable options for the unloader valve. Air pressure from the Governor opens the unloader valves to unload or stop compression in the compressor.
In a system with an unloading diaphragm, air under pressure passes into a cavity below the Governor when the reservoir air pressure reaches the Governor’s maximum setting. This air pressure causes the unloading valves to open by lifting one end of the unloading lever, which pivots on its pin.
The unloading cavity creates a passageway between the cylinders above the pistons when the unloading valves are removed from their seats. Compression is then ceased while air circulates back and forth across the space between the cylinders. When the air pressure falls below the Governor’s minimum setting, it releases the pressure from underneath the unloading diaphragm, allowing the unloading valves to re-engage and resume compression.
Symptoms of a Bad Air Governor
The Governor controls the compressor. It puts it into the load phase, as it is called in Ontario and other jurisdictions, as part of its operation. But what if your Governor is a bad one? How will you understand that?
The answer is pretty simple. When you try to operate it, you will notice some symptoms. As you try to start or stop it, you’ll notice that it doesn’t want to start or stop, which is an obvious sign of a bad governor. If you can manage to start it, soon you will hear odd noises from the compressor, and it will shake. If you have a circuit breaker problem, warm air will flow through the system, and you will find moisture in or around the system.
Conclusion
Finally, an air compression governor is an essential mechanical part of any motor. Therefore, the electric motor drive’s functioning is controlled, and the failure of moving parts is avoided with the aid of the compressor regulator.
Also, the air compressor governor is an important part of an industrial machine and can have a significant impact on the performance of the machine. By understanding “what does the air compressor governor do”, users can optimize their machines for better results.

